Induction Heating
What is Concept of Induction Heating :
- Induction heating is one of the most widely used electrical heating methods in industrial applications.
- Generally it is applicable for many heating processes of the metals because it works on eddy current generation principle.
- In this method high frequency AC supply is used so it becomes a type of RF heating method.
Principle of Induction Heating
- Induction heating operates on the principle of "induction" in order to heat an electrically conducting material.
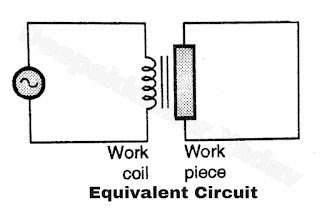
- The material to be heated is known as the work piece and the coil wound around it is known as work coil as shown in Figure A.
- The work coil will act as primary winding and the work piece will act as short circuited secondary winding of a transformer as shown in Figure B.
- When a high frequency ac voltage is applied across the work coil, a magnetizing current flows through it.
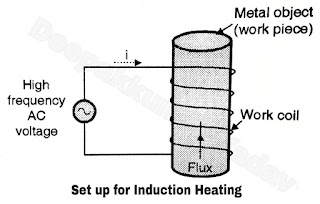 | ||||
Figure A
|
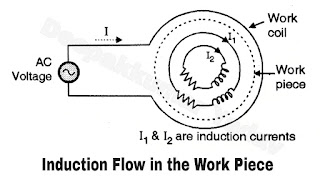
- This will generate flux in the work piece and induce voltage into the work piece. Since the work piece is closed onto itself, induction current flows into it as shown in Figure C.
- Due to the finite resistance offered by the work piece to the flow of the induction current, the work piece will be heated up. Thus induction heating is actually an induction current heating.
- The heat loss in the work piece is normally confined to surface of the work piece due to "SKIN EFFECT". It is the tendency of current to get concentrated at the surface. "SKIN EFFECT" is observed at higher frequencies of operation.
- Therefore as we go deeper into the work piece the induction current reduces.
- This has been shown in Figure D.
- As seen from Figure D the induction current density reduces in an exponential manner with increase in the distance (x) from the surface of the work piece.
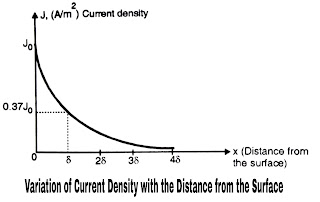 |
| Figure D |