Definition and Principle of Dielectric Heating
Definition of Dielectric Heating :
Dielectric heating is another type of RF heating. It makes use of the dielectric loss in imperfect dielectric materials and is therefore, suitable for heating non-metals.
Principle of Dielectric Heating :
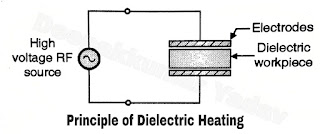
- In dielectric heating, a high frequency, high voltage ac voltage is applied across a dielectric material.
 |
| Figure A |
 |
| Figure B |
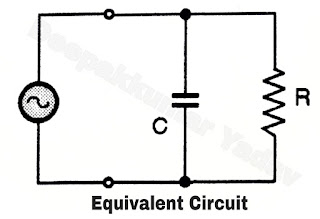
- The dielectric workpiece is held between two metal electrodes as shown in Figure. The dielectric material can be plastic, wood etc.
- Due to the high voltage RF excitation, some current flows through the dielectric material and due to this current flow some loss takes place in the dielectric which is called as "dielectric loss".
- This power loss takes place in the form of heat and the dielectric material gets heated up due to it. This is the principle of dielectric heating.
- The power loss taking place in a dielectric material is given by the following equation :
Po = 0.55 x 10-12f[V/b
cm]2
Where, F = Frequency of operation.
V = Applied Voltage.
b = Thickness of the dielectric workpiece
The power loss per unit volume (Po) in a dielectric slab depends upon following factors :
- It increases with increase in frequency of operation.
- It increases with the square of voltage gradient, (V/b cm)2 and
- It depends upon the constants of the dielectric material through the loss factor, (€ r tan ).