Classification and applications of Inverters
Classification of Inverter Based on the Nature of Source :
- The inverters can be classified on the basis of a number of factors, the first one being the type of source it uses at its input.
- Depending on the nature of input power source the inverters are classified into two categories :
- Voltage Source Inverters (VSI).
- Current Source Inverters (CSI).
- In case of VSI the input to the inverter is provided by a ripple free dc voltage source, where as in CSI the voltage source is first converted into a current source and then used to supply the power to the inverter.
 |
| Figure A |
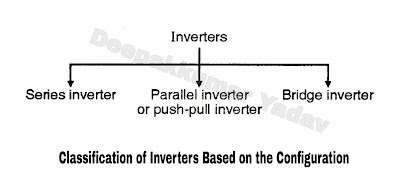
Classification Base on the Configuration of the Inverter :
- The Voltage Source Inverters (VSI) are classified based on the arrangement of thyristors in the power circuit. The configurations are:
- Series inverter.
- Parallel inverter or push pull inverter.
- Bridge inverter. (half bridge or full bridge).
- Any one of these configurations is selected depending on the applications. The bridge configuration however is the most widely used one.
 |
| Figure B |
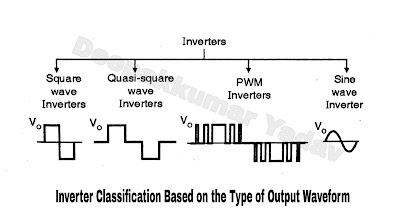
Classification of Inverter Based on the Nature of Output Waveform :
- The inverter output ac waveform need not always be a sine wave. It can be a square wave, a quasi square wave or a pulse width modulated waveform.
- Filters may be used to derive a sine wave from the square or quasi square wave output.
- The percentage of harmonic frequency components largely depends on the shape of the output waveform.
 |
| Figure C |
Classification of Inverter Based on Type of Commutation Circuit :
- For thyristorised VSI, there are different types of forced commutation circuits available. The two popularly used commutation circuits are :
- Auxiliary commutation (Mc Murry Bedford circuit) and
- Complementary commutation (Mc Murry circuit).
- The commutation circuits must be designed to successfully commutate the thyristors, with minimum consumption of power in the commutation components. The type of commutation may be voltage commutation or current commutation. The design of commutation components must be optimized to maximize the efficiency of the inverter.
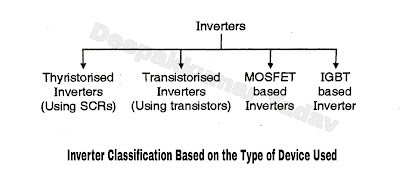
Classification Based on the Power Semiconductor Device Used in Inverter :
- We can use any power semiconductor device as a switch to construct an inverter. The devices normally used are : SCR, power transistor, power MOSFET, IGBT. The classification is as given in Figure D.
Applications of Inverters :
- In the UPS systems.
- In the speed control of ac motors.
- In induction heating.
- In emergency light systems.
- In HVDC transmission.
- In the communication equipments.