Spray Ponds and Cooling Towers in Thermal Power Plant
Q. What are cooling towers used for in a thermal power plant?
Q. What are water cooling towers used for?
Q. How do power plant cooling towers work?
(A) Spray Ponds
- Spray ponds are generally used for small thermal projects. They are used for cooling the condensate from the condenser.
- In this case, the hot water is distributed throughout the pond and is sprayed in air at a pressure. By spraying at high pressure the condensed water transfers heat by convection and evaporation, as the sprayed water comes in contact with the atmospheric air, it is cooled.
- Mostly, the water is cooled by evaporation. The heat for evaporation is obtained from water. For this purpose, it is necessary that a large surface of water is exposed.
- The nozzles used for spraying should be such that they must produce the spray of water and not the sheet of water.
- The spacing between them should be about 2.5 to 3 m and should be placed 2 to 3 m above the pond water.
- The nozzles provided should be adjustable according to load and climatic conditions.
(B) Cooling Towers
Cooling of condensed water from the condenser is carried out by following methods :
(i) Natural draught cooling towers.
(ii) Forced draught cooling towers.
(I) Natural draught cooling towers :
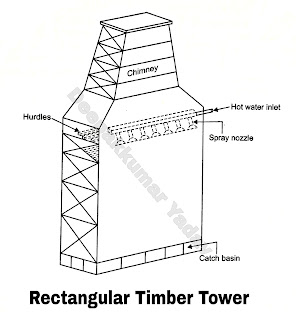
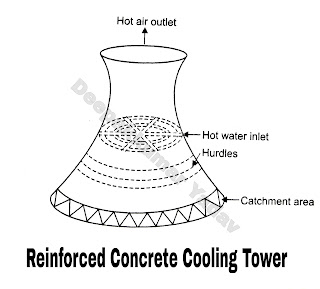
The condensate water from the condenser to be cooled is pumped at about 10 m above the ground into the troughs and the nozzles at the bottom of the troughs, sprayed it in thin sheets. These thin sheets of water break under force of gravity and when it strikes with the hurdles. The circulation of air for cooling the water is induced by enclosing the heated air in the chimney. As the heated air is lighter than the surrounding air of atmosphere it produces a difference of pressure causing natural draught of air for cooling of water. There are two types of construction of natural draught cooling towers :
(a) Rectangular timber tower as shown in Figure A.
(b) Reinforced concrete hyperbolic type as shown in Figure B.
The concrete type have the following advantages :
(i) Better circulation of air.
(ii) wide variation of load is possible as much larger amount of water per hour can be cooled.
(iii) Maintenance cost is less.
(iv) No fire hazard.
 |
| Figure A |
 |
| Figure B |
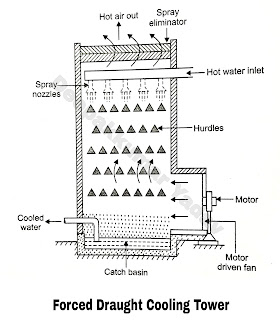
The forced draught cooling towers have horizontal shaft fan on the side of the cooling tower. This fan discharges air towards the back of tower and then it is turned upwards by means of baffles. In the process it cools the falling water. Fan speeds of the order of 100 rpm are used for this purpose.
The Induced draught type cooling towers are used for large capacity Installations They use large fans with vertical shaft located at the top of the towers, and they pull air upwards from the sides of the cooling tower. The warm air is exhausted at a considerable velocity upwards after cooling the water on its way. It requires low speed fans.
 |
| Figure C |