The electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom are usually not securely bound to the nucleus and therefore may fly off the atom (Figure A) and move into an outer orbit of another atom. These relatively free electrons normally move at random in all directions. However, when an electrical pressure (voltage) is applied across a length of wire, the free electrons in the wire give up their random motion and move or flow in one general direction. This flow of free electrons in one general direction, shown in Figure (B), is called an electric current or simply current."
 |
| Figure (A) |
FIGURE (A) Atom showing electron in outer orbit leaving atom. The atom then has more positive charge than negative charge. The nucleus will therefore attract some other free electron that moves into its vicinity.
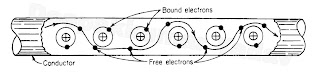 |
| Figure (B) |
FIGURE (B) Flow of free electrons in a conductor. Only electrons in the outer orbit are free to move from one unbalanced atom to another unbalanced atom. This flow or drift of free electrons is called an electric current.

