Static (I-V) Characteristics of MOS Controller Thyristor (MCT)
In the static condition, the I-V characteristics of the MCT are similar to those of SCR and GTO.
Switching Characteristics of MOS Controller Thyristor (MCT)
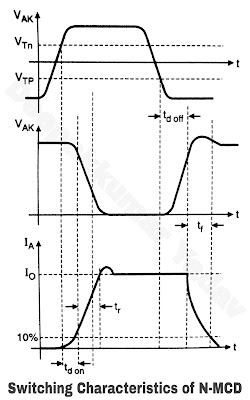
- MCT can change its state from ON to OFF or OFF to ON within 1 µsec. Figure (a) shows a switching circuit using an N-MCT and Figure (b) shows the switching waveforms of the device.
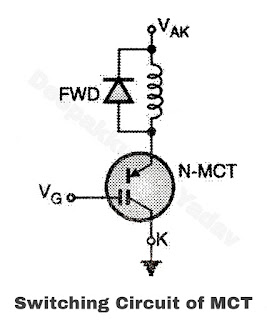
Figure (a)
The total turn on time is equal to the sum of two different time durations :
(a) Turn on delay time (td on)
(b) The current rise time (tr)
(a) Turn on delay time (td on)
- It is equal to the time taken by the anode current to increase to 10% of its maximum value Imax. This delay time corresponds to the time required for the injection of excess carriers before the beginning of the regenerative action. Typically td on = 0.5 µS.
(b) Rise time
- This is the time required for spreading of the plasma of excess carriers under the gate electrode. Typically tr = 0.5 µS.
- During the turn on process of MCT, we can connect a small series inductance as the turn on snubber as shown in Figure (a) in order to protect it against high di/dt rate.
2. The turn off time
- The turn off time is equal to the sum of two different time durations :
(a) The delay time td off
(b) The fall time tf
(a) The delay time td off :
- This time corresponds to the time taken by anode to cathode voltage to reach its off state value. Typically td off ≤1 µsec.
- It is the time required for the recombination to take place in the base regions. Typically tf = 0.5 to 1 µS.
Ratings of MCT
- Ratings : 1000 V / 100 A
- Can be turned on and off by applying small negative and positive voltages respectively to the gate.